#10 Functions (String, Date, Numeric)
SQL Crash Course #10
All the course material is stored in the SQL Crash Course repository.
Hi everyone! Cornellius and Josep Ferrer from DataBites here 👋🏻
As promised, today we are publishing the next two issues of our SQL Crash Course – From Zero to Hero! 🚀
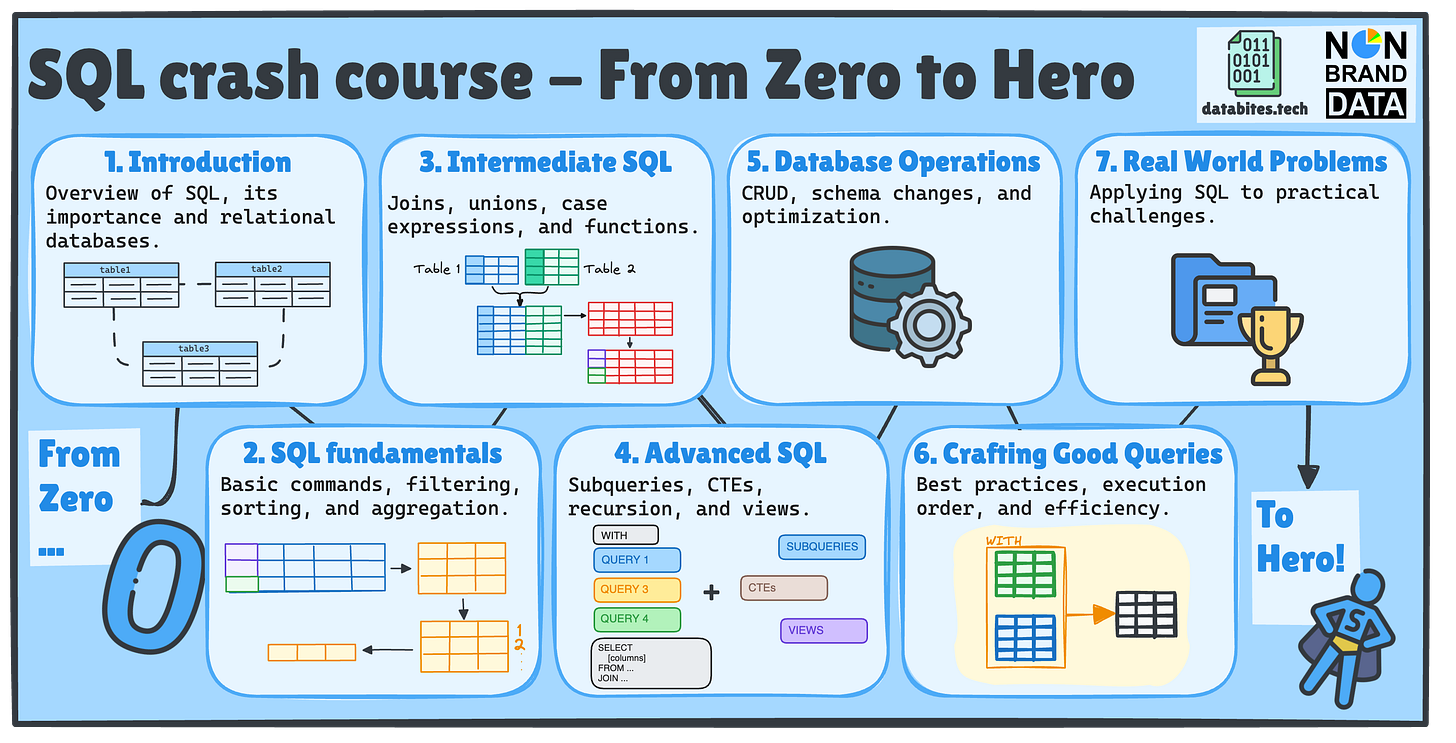
I am sure you are here to continue our SQL Crash Course Journey!📚
If this is your first time or you’ve forgotten what we’ll cover, we will examine seven key SQL topics, each divided into multiple posts across Non-Brand Data and DataBites.
📚 Previously in SQL Basics…
Remember last Thursday we already saw
📌 #7 – JOINS (INNER, LEFT, RIGHT, FULL) by Josep in DataBites
📌 #8 – UNION & UNION ALL by me in Non-Brand Data.
Today, two fresh issues just dropped:
📌 #9 – Case Expressions – In this lesson, Josep will explain all about combining CASE expressions in SQL.
📌 #10 – Functions (String, Date, Numeric) – where we will explore how to work with SQL functions.
So don’t miss out—let’s keep the SQL momentum going!
What are SQL Functions?🤔
SQL functions let you manipulate data directly in your queries. Instead of exporting data to Python or Excel for cleaning or calculations, you can:
Format text dynamically
Calculate dates and the related data
Round numbers, aggregate values, or extract patterns
Everything was done while staying in your SQL workflow.
Functions are in the form of predefined operations that take inputs, process them, and return results. They fall into three core categories:
String Functions: Clean, slice, or format text.
Date Functions: Handle dates and times effortlessly.
Numeric Functions: Crunch numbers with precision.
All the functions have a standard usage where:
SELECT
FUNCTION(data) AS function_result
FROM table; The difference is that each function will have different usages and outputs. To understand them all, refer to the SQL Functions List documentation.
Let’s break them down!👇
🔧 String Functions
Use Case: Format names, clean messy text, or extract substrings.
String functions are methods used for applying text data manipulation to the data. They are applicable to any string data available in our database.
Let’s take a look at the common String Functions with examples.
1. CONCAT
Combines two or more strings into a single string.
SELECT
CONCAT(n.name, ' - ', p.name) AS combined_title
FROM posts p
JOIN newsletters n ON p.newsletter_id = n.id; 🧠 Use Case: Perfect for creating human-readable report titles (e.g., combining newsletter and post names for dashboards).
2. SUBSTRING
Extracts a portion of a string based on a starting position and length.
SELECT
SUBSTRING(name, 1, 5) AS short_name
FROM posts; 🧠 Use Case: Generate post ID abbreviations for analytics tools or URL slugs.
3. UPPER/LOWER
Converts text to uppercase or lowercase to standardize formatting.
SELECT
id,
UPPER(name) AS uppercase_name
FROM newsletters; 🧠 Use Case: Standardize text for case-sensitive systems (e.g., integrating with APIs or CRM tools).
4. TRIM
Removes leading and trailing whitespace from a string.
SELECT
id,
TRIM(type_of_interaction) AS clean_type
FROM interactions; 🧠 Use Case: Clean messy user inputs before exporting data to visualization tools like Tableau.
5. REPLACE
Replaces instances of a substring with a new value.
SELECT
id,
REPLACE(name, 'DataBites', 'DB') AS renamed_post
FROM posts; 🧠 Use Case: Fix branding inconsistencies in exported CSV files for stakeholders.
📅 Date Functions
Use Case: Calculate deadlines, filter date ranges, or extract year/month/day.
Like the String Function, Date Functions are mostly applicable for manipulating any datetime data.
Here are the common Date Functions you should know about.
1. CURRENT_DATE
Returns the current date (today) to filter or compare against time-sensitive data.
SELECT
name,
published_at
FROM posts
WHERE published_at = CURRENT_DATE; 🧠 Use Case: Power real-time dashboards showing "Today’s Publications."
2. EXTRACT
Retrieves a specific part of a date (e.g., year, month, or day) for trend analysis
SELECT
name,
EXTRACT(YEAR FROM published_at) AS publish_year
FROM posts; 🧠 Use Case: Aggregate content performance by year for annual reports.
3. DATE_ADD
Adds a specified time interval to a date.
SELECT
post_id,
datetime
FROM interactions
WHERE datetime >= DATE_ADD(CURRENT_DATE, INTERVAL -7 DAY); 🧠 Use Case: Track weekly engagement trends in growth/marketing dashboards.
4. DATEDIFF
Calculates the number of days between two dates.
SELECT
name,
DATEDIFF(CURRENT_DATE, published_at) AS days_since_published
FROM posts; 🧠 Use Case: Identify stale content needing updates in editorial calendars.
➗ Numeric Functions
Use Case: Round values, calculate averages, or find remainders.
Lastly, the Numeric Functions are applicable for any numerical procedure that happen in our data.
These are the common Numeric Functions that will be useful for your work.
1. SUM
Totals numeric values across rows.
SELECT
post_id,
SUM(points) AS total_points
FROM interactions
GROUP BY post_id; 🧠 Use Case: Calculate total engagement scores for leaderboards or rankings.
2. AVG + ROUND
AVG help computes the average of numeric values while ROUND rounds a number to a specified decimal place.
SELECT
post_id,
ROUND(AVG(points), 1) AS avg_points
FROM interactions
GROUP BY post_id; 🧠 Use Case: Compare average user engagement across posts in performance dashboards.
3. CEIL/FLOOR
Rounds a number up (ceiling) or down (floor) to the nearest integer.
SELECT
post_id,
CEIL(SUM(points)) AS ceil_points,
FLOOR(SUM(points)) AS floor_points
FROM interactions
GROUP BY post_id; 🧠 Use Case: Simplify rounded metrics for executive summaries or KPI slides.
4. ABS
Returns the absolute (non-negative) value of a number.
SELECT
id,
ABS(points - 5) AS diff_from_five
FROM interactions; 🧠 Use Case: Measure deviation from a target score (e.g., quality control checks).
5. MOD
Returns the remainder after division.
SELECT
id,
MOD(points, 2) AS is_even
FROM interactions; 🧠 Use Case: Flag even/odd values for A/B testing splits or sampling strategies.
🔄 Bonus: Combine Functions
We can combine FUNCTION within the same query to produce the desired result. For example, we use CONCAT, DATEDIFF, CURRENT_DATE, ROUND, and AVG in the same query.
SELECT
p.name AS post_name,
CONCAT(n.name, ' #', p.id) AS newsletter_post,
DATEDIFF(CURRENT_DATE, p.published_at) AS days_old,
ROUND(AVG(i.points), 1) AS avg_engagement
FROM posts p
JOIN newsletters n ON p.newsletter_id = n.id
LEFT JOIN interactions i ON p.id = i.post_id
GROUP BY p.id, n.name; 🧠Useful when you have a complex data requirements that need to follow certain standards.
✅ Summary: Use SQL Functions When You Want To…
Format or clean text
Manipulate dates
Crunch numbers
Aggregate and analyze metrics
Simplify complex data transformations
Standardize outputs
👉Also, don’t miss the SQL Playground for this issue!
How to Get Started 🚀
Over the coming weeks, we’ll guide you through:
✅ SQL Fundamentals
✅ Intermediate SQL
✅ Advanced SQL
✅ Database Operations
✅ Writing Efficient Queries
Once you grasp the basics, practice is key! Start working on real-world projects and solving hands-on data problems.
What’s Next? ➡️
This is the first of many posts about the upcoming SQL Courses. It will only explain what SQL is in its crude form.
To get the full experience and fully immersed in the learning:
👉 Subscribe to Databites.tech (By Josep)
👉 Subscribe to Non-Brand Data (By Cornellius)
👉 Check out the SQL Crash Course GitHub repo
👉 Share with your friend and whoever needs it!
🗓️ Every Thursday, you will have two new issues in your inbox!
Let’s dive in and make SQL less scary, more fun, and way more useful! 🚀
Josep & Cornellius
🎉 We celebrate 7,275 subscribers with a 20% lifetime discount on the annual plan.
Only until April 19, 2025.
👉 Grab it here:
Because sometimes… numbers deserve a party.