LLMs Can Perform Regression Modeling Tasks
Extend the power of Large Language Model for Regression
Large Language Model or LLM is a model that could process and generate human-like text based on the data on which it has been trained.
LLM has been trained extensively to perform text-based tasks such as question-answering and summarization to generate code. The model has been specifically developed to help the user in the language works.
Several experiments utilize LLM as a classic model tool, such as classification. For example, text-classification use cases were familiar with LLM.
There are not many use cases for LLM with tabular data. However, using LLM in the tabular data modelling task is possible. Previously, I have written about using the LLM for classification tasks in my newsletter below.
Recently, there has been a new experimental approach to implement LLM for Regression tasks. This approach shows an outstanding result that might be potentially a game changer.
How does it work then? Let’s get into it.
LLM For Regression
In the machine learning field, Regression is the task of predicting infinite numerical values from the given input. In contrast, classification tasks only try to predict from the finite values.
Regression tasks have been traditionally performed using classic models such as linear regression in tabular data. However, research by Vacareanu et al. (2024) has shown that LLM can perform regression tasks given the Few-Shot example context.
Their experiment showed that the Mean Absolute Error from the LLM model could match or even better than some of the traditional models. You can see the result in the image below.
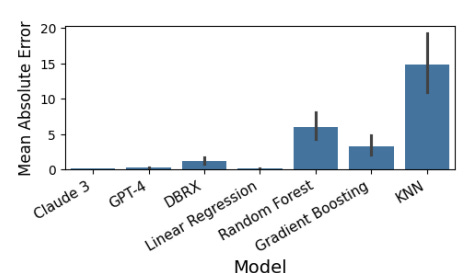
The researcher also experiments with several model comparisons in three different datasets.

The result above reveals that LLM models, whether closed-source (e.g., Claude 3, GPT-4) or open-source (e.g., DBRX, Mixtral 8x7B), can perform linear regression tasks using in-context learning.
Now, how do we perform linear regression with LLM? Let’s get into it in the next section.



